Decoding the Blueprint of Ageing: The Vital Importance of the 12 Hallmarks in Slowing Down the Ageing Process
Introduction
Ageing is a natural part of life, but researchers have long sought to understand the underlying mechanisms that drive it. Enter the "12 Hallmarks of Ageing," a comprehensive framework that sheds light on the complex processes that contribute to growing older. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of these 12 hallmarks and how understanding them is crucial in our quest to slow down the ageing process.
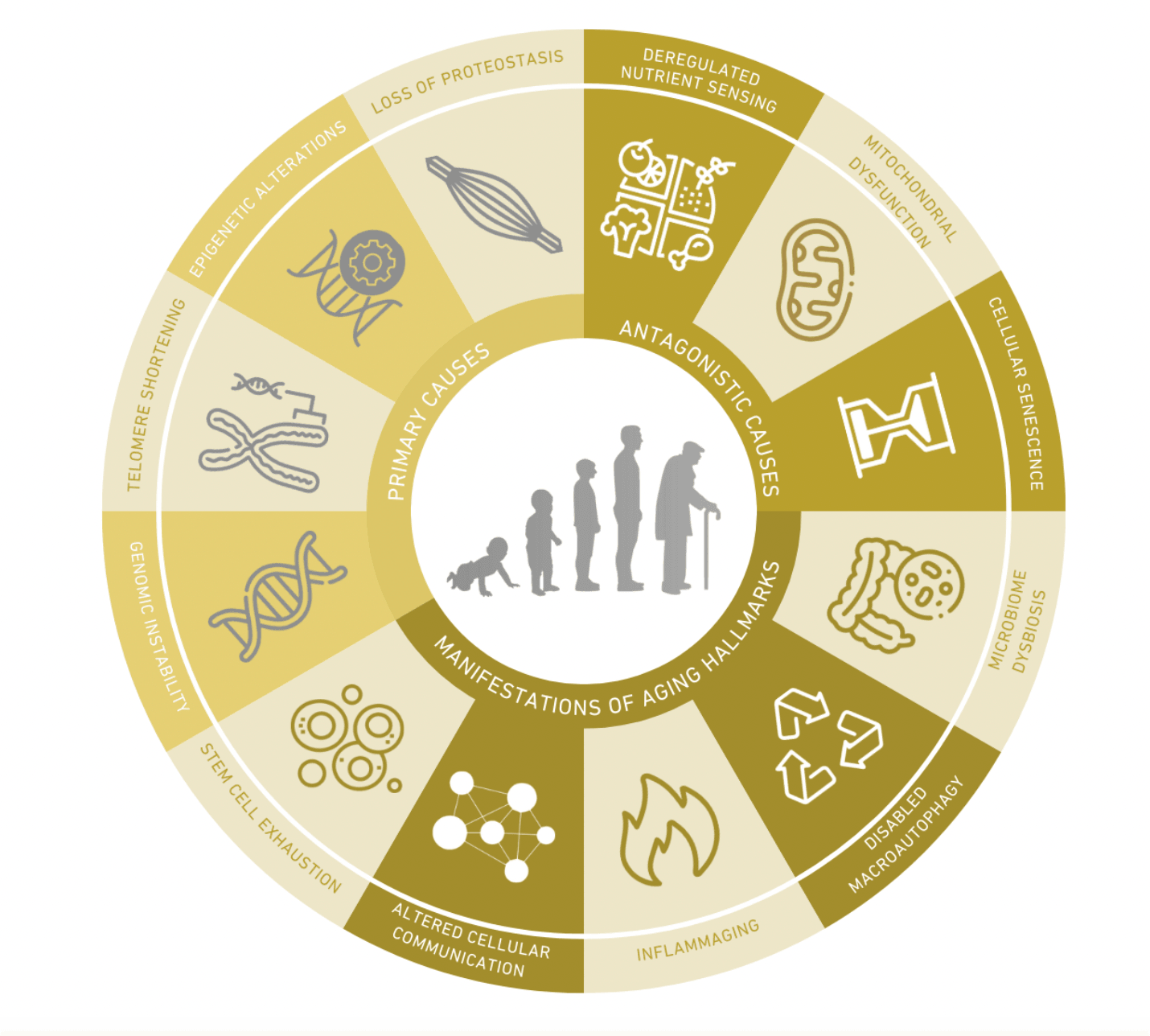
1. Genomic Instability
Genomic instability refers to the cumulative damage and mutations that occur in our DNA over time. It can lead to cell dysfunction, cancer, and other age-related diseases. By studying genomic instability, researchers can develop strategies to repair and protect our DNA, thus slowing down the ageing process.
2. Telomere Shortening
Telomeres, protective caps at the ends of our chromosomes, naturally shorten as we age. This shortening is associated with cellular ageing and age-related diseases. Finding ways to maintain telomere length or slow their erosion is a key focus in anti-ageing research.
3. Epigenetic Alterations
Epigenetic changes, which regulate gene expression without altering DNA sequences, can impact how our genes function over time. Understanding and potentially reversing these alterations could have a profound impact on slowing down the ageing process.
4. Loss of Proteostasis
Proteostasis involves maintaining proper protein folding and function within cells. Age-related protein misfolding and aggregation contribute to diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Strategies to preserve proteostasis hold promise in mitigating these conditions.
5. Deregulated Nutrient Sensing
The body's ability to sense and respond to nutrients declines with age, impacting metabolism and overall health. Interventions aimed at restoring nutrient sensing can help improve health and longevity.
6. Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Mitochondria, the cell's powerhouses, can become dysfunctional with age, leading to energy depletion and oxidative stress. Strategies to enhance mitochondrial function are essential in combating age-related decline in energy levels and overall health.
7. Cellular Senescence
Cellular senescence is when cells lose their ability to divide and function properly. These senescent cells can promote inflammation and tissue damage. Senolytic therapies aim to remove these harmful cells and promote healthier ageing.
8. Stem Cell Exhaustion
Stem cells are essential for tissue repair and regeneration. As they decline in number and function with age, developing ways to rejuvenate or replace them becomes crucial for maintaining tissue health.
9. Altered Intercellular Communication
Age-related changes in signaling pathways can lead to chronic inflammation and other health issues. Modulating intercellular communication can help reduce inflammation and promote better health in old age.
10. Inflammaging
Chronic, low grade, systemic inflammation plays a pivotal role in the development of atherosclerotic heart diseases, cancer and neurodegenerative condition e.g. Alzheimer’s disease
11. Disabled Macroautophagy
Macroautophagy is a cellular process, responsible for removing and recycling damaged cell components. When this process is disrupted, it can lead to the accumulation of waste in our cells, potentially contributing to diseases, including neurodegenerative conditions and metabolic disorders.
12. Microbiome Dysbiosis
Imbalance of natural microbial community, reduction of beneficial kind and overgrowth of the harmful kind leads to brain dysfunction, poor immune health, and chronic inflammation.
Conclusion
The 12 Hallmarks of Ageing serve as a comprehensive roadmap for understanding the intricate processes that drive the ageing process. By unraveling these hallmarks and developing targeted interventions, scientists and researchers are striving to slow down ageing and extend healthspan—the period of life spent in good health.
While we cannot entirely halt the march of time, our growing knowledge of these hallmarks provides hope for a future where we can age with grace and vitality. By embracing a holistic approach to health that incorporates anti-ageing strategies based on these hallmarks, we have the potential to enhance the quality of our later years and enjoy a longer, healthier life.



